
Fish, including shellfish, can be a healthy part of your child’s diet soon after they begin to eat solid foods, usually around 6 months old. Because both are common allergens, it’s best to wait until your baby has tried a few other low allergy foods and has had no reactions (like baby cereal and pureed fruits and vegetables) before introducing fish or shellfish.
Fish is a good early food because it’s full of important nutrients, including protein and fatty acids. But it’s best to avoid some types of fish because they can contain unsafe levels of mercury, which in high doses can be harmful to children.
Is fish healthy for babies?
Fish can have an important role in a balanced diet – it’s full of nutrients that are crucial for a child’s health and development.
Fish is a healthy source of protein and lipids (fats). Lipids serve as an energy source, provide padding for vital organs and protection from temperature extremes, and allow absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Fish contains omega-3 fatty acids that are important for brain development, vision and eye formation, the immune system, and a healthy heart. Fish can be a source of vitamins D, E, B1, B3, B6, and B12; it also contains calcium, iron, and fluoride.
What kind of fish is best for babies?
Certain types of fish contain high levels of methylmercury, a metal believed to be harmful in high doses to a child’s developing brain and nervous system. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has a list of which types of fish are best to give children, based on the fish’s mercury level. Experts recommend children 1 to 3 years old get two to three 1-ounce servings of the “best fish” each week, and just one serving of “good fish” each week.
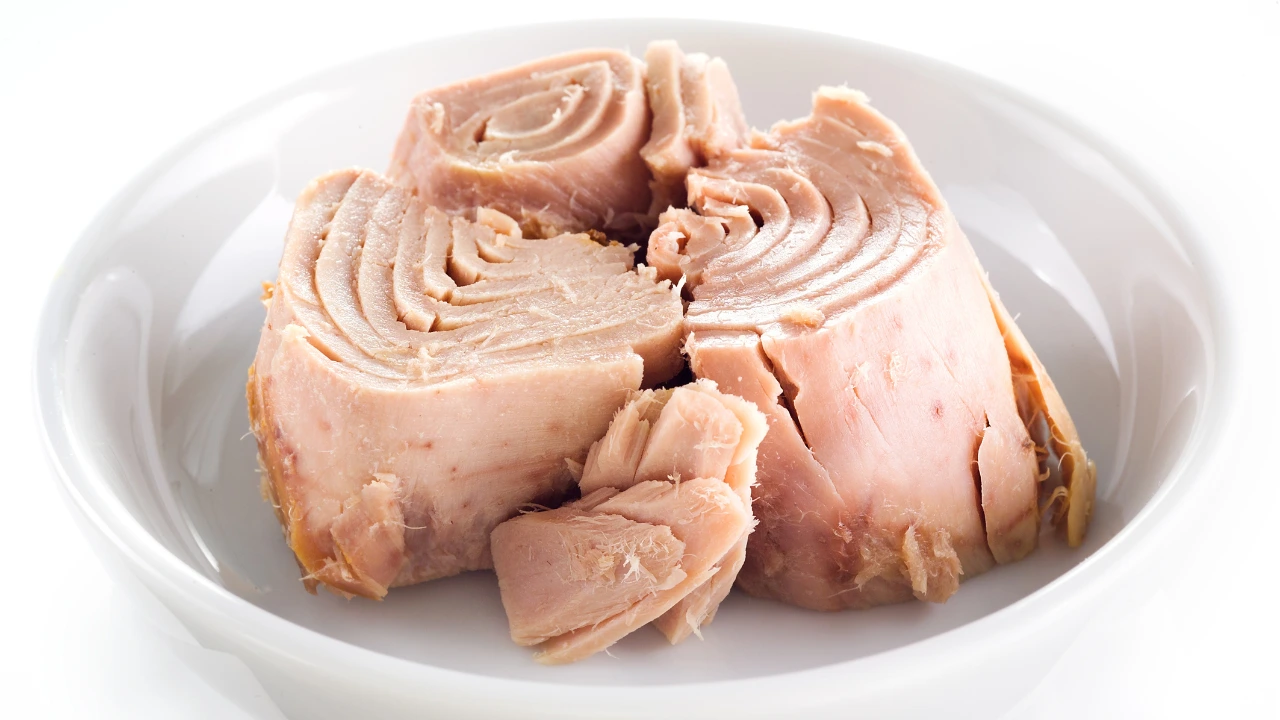
For example, salmon is considered “best” and can be given to your baby multiple times a week, since it has very low levels of mercury. Canned tuna, a “good” option, is best limited to once a week because of its potential mercury content. And don’t give your baby large fish, like swordfish, at all, since they are higher in mercury.
The best fish to give your baby:
- Catfish
- Cod
- Crab
- Haddock
- Salmon
- Sardine
- Scallops
- Shrimp
- Tilapia
- Whitefish
Good fish:
- Albacore tuna (used in canned tuna)
- Carp
- Halibut
- Mahi mahi
- Snapper
Fish to avoid:
- Bigeye tuna
- King mackerel
- Marlin
- Orange roughy
- Tilefish
- Shark
- Swordfish
When can babies eat asa lebleb?
Only give your baby asa lebleb made with fully cooked fish. Raw or undercooked fish may be a source of bacteria or toxins, although it’s uncommon that they cause illness in children.
It’s also best to avoid asa lebleb made with types of fish that can have high mercury content, regardless of whether or not it’s cooked.
Asa lebleb in awasa is typically sliced fish, which is likely going to be too tough for your baby to chew well and could pose a choking hazard. If you feed your baby asa, consider chopping it very small pieces and well cooked so your baby can eat it more easily.
Can babies be allergic to fish?
Both fish and shellfish are among the most common foods people are allergic to. While babies often grow out of food allergies as they age, it’s less common for fish or shellfish allergies to go away. Seafood allergies are also more likely to cause severe reactions than other food allergies.
Fish and shellfish are different categories of allergens – so if a baby is allergic to fish, they might not be allergic to shellfish and vice versa. It is possible to be allergic to both fish and shellfish, though. The same goes for different types of fish: Being allergic to one type (say, salmon) doesn’t necessarily mean a baby will be allergic to another (like tuna), though it’s possible to be allergic to all kinds of fish.
When introducing a potentially allergenic food, experts recommend giving it to your baby at home, rather than at daycare or a restaurant. As with any new food, serve it for three to five days before offering another new food. That way you can monitor your baby for a reaction and know what’s likely causing it.
Signs of a food allergy include hives, itchy skin rashes, swelling, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and pale skin. If you notice any of these symptoms in your baby, let their doctor know. If your baby has symptoms that involve multiple parts of the body (such as hives with vomiting or diarrhea), it could be an anaphylactic reaction and you should immediately call emergency number.
Other signs of an anaphylactic reaction are throat tightness, breathing problems, wheezing, lightheadedness, and loss of consciousness. If your baby shows signs of an anaphylactic reaction after eating fish, call emergency number or go to an emergency room immediately.
How to serve fish to your baby
When preparing fish for your baby, remove all the skin and any bones (including very small ones inside the meat), and puree or mince it into small pieces to prevent choking. Once your baby shows signs of readiness for finger foods (between 8 and 10 months), you can serve them bite-sized pieces of cooked fish.
When you give your baby shellfish, be sure to completely remove the shell and any hard pieces, such as shrimp tails, to prevent choking. Shellfish often has a tougher texture than other fish, so cut it into small pieces, around a quarter of an inch, or puree it when you serve it to your baby,
Add a Comment