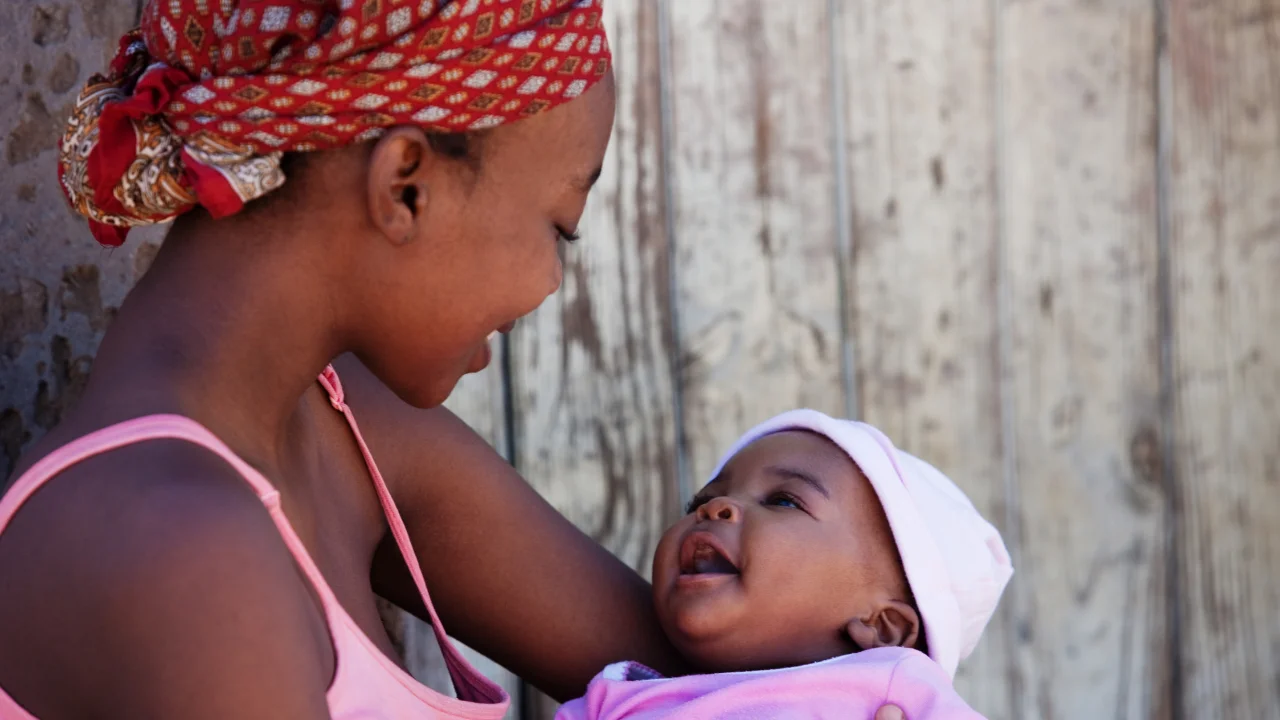

Breastfeeding problems shouldn’t hurt unless there’s a problem – but there are plenty of breastfeeding problems that can pop up, especially in the beginning. Common issues for breastfeeding moms include sore nipples, clogged ducts, and engorgement. Your breasts may leak, or you may worry about your milk supply. Your baby may prefer one breast over the other, or they may go on a nursing strike. The good news is that there are plenty of solutions for breastfeeding problems – and many sources of support.
IN THIS ARTICLE
- Why is breastfeeding so hard?
- Does breastfeeding hurt?
- Common breastfeeding problems
- How to find breastfeeding support
Breastfeeding can be enjoyable for both you and your baby, but it can also be challenging – especially in the first few weeks. Below are descriptions of common breastfeeding problems difficulties as well as links to more information and advice.
Why is breastfeeding so hard?
Breastfeeding isn’t always hard. Sometimes the whole process goes smoothly and comfortably, and a mom and baby breastfeed for months or years without a hitch. But breastfeeding problems often comes with challenges, big and little. Your baby may take some time to learn to latch on, for example, or you may struggle with milk supply, pain, or infection. Complications like these often come at the beginning of your breastfeeding journey, which can be especially discouraging.
Ironing out breastfeeding problems complications can be tiring and time-consuming, but the health benefits of breastfeeding – for you and your baby – are worth the effort. And once you get over the hump, breastfeeding usually gets much easier. Most moms also find it more convenient, more economical, and more enjoyable than making bottles.
Be sure to contact your healthcare provider or a lactation consultant for help and support with any breastfeeding problems.
Does breastfeeding hurt?
Breastfeeding shouldn’t hurt. If it does, it’s a sign that something’s wrong. Most often it’s because your baby isn’t latching well (see below). A lactation consultant can help you determine if that’s the case and show you how to correct your baby’s latch.
Other issues that cause discomfort can pop up, too, such as:
Painful letdown
A tingling sensation is typical when the milk ducts in your breasts constrict to pump milk into the nipples (this is called letdown). But some women have pain during letdown.
This can happen if you’re producing too much milk, or if you have clogged ducts or mastitis (an inflammation of breast tissue). It can also happen if you have a thrush on your nipples/breasts. Use breathing or relaxation techniques to cope, and see your provider if you have any signs of infection, such as a fever or itchy, red, or burning nipples.
Nipple vasospasm
Restricted blood flow caused by tightening blood vessels in your breasts can cause a burning or stabbing pain. You may notice that your breasts become blanched and your nipples change color (become more purple or red). Having cracked nipples or an infection can make the pain worse. Keeping your breasts warm and avoiding caffeine may help. But see your healthcare provider or lactation consultant to get to the underlying reason for the vasospasms. They may recommend medication.
Teething
Your baby may get new teeth without it affecting breastfeeding problems in the least. But – in an effort to adjust because of the pain they feel on their gums when nursing – they may change position or latch, or even bite to relieve the discomfort.
Pay attention to your baby’s latch, and experiment with different breastfeeding positions. Anticipate a bite, when you can (you may notice your baby moves their tongue out of the way first), and unlatch your baby by putting your finger in the corner of their mouth. Massaging your baby’s gums or giving them a teether before nursing may help.
Sensitive nipples
Tender nipples are often an early sign of pregnancy or an imminent menstrual period. And some breast surgeries may result in numbness or even pain in your nipple or breast, because of nerve damage. Having your baby latch on when your nipples are feeling sensitive can be very uncomfortable. To avoid nipple pain, make sure your baby has a good latch (they aren’t sucking on the end of your nipple, for example).
Postpartum cramping
After you deliver your baby, your uterus needs to return to its pre-pregnancy size. You may feel some cramping when this happens, and the cramping may be especially intense while nursing. That’s because breastfeeding can stimulate uterine contractions – which is good, though sometimes painful.
Breathing exercises and massage may help you get through the cramping. If needed, you can also take over-the-counter pain relievers to help with the pain, which should disappear within a week or so.
Some of the common breastfeeding problems below can cause pain, too.
Common breastfeeding problems
Sore, cracked, or bleeding nipples
Despite being very common, sore nipples aren’t a normal part of nursing that you have to endure. Sore, cracked, or bleeding nipples are most often caused by a poor latch (see below). But a yeast infection, incorrect use of a breast pump or flanges that don’t fit well, or very dry skin or eczema can also be to blame.
Reach out to your provider or lactation consultant right way so you can get to the bottom of the cause and work on a solution. Keep breastfeeding, if you can, to prevent engorgement. And contact your provider if you have any signs that your cracked or bleeding nipples are infected, such as fever, inflammation, oozing, or pain that radiates to the breast.
Poor latch
In the beginning, it’s normal for breastfeeding problems to hurt when your baby is latching. But it should feel better after 15 to 30 seconds, as your baby draws the nipple deeper into their mouth. If it continues to hurt, it may be because your baby has a consistently shallow latch.
If your baby doesn’t latch well, it can cause all kinds of problems. Because your baby may suck on the ends of your nipples, they can become painful and crack and bleed. You may wind up with clogged milk ducts, mastitis, and low milk supply. Your baby may not get enough milk.
Have a lactation consultant evaluate your baby’s latch if you have any questions. They can identify problems and help you address them. Sometimes a simple adjustment in how you position yourself and your baby when breastfeeding can make all the difference.
Read more about how to get a good breastfeeding latch and why it’s so important.
Engorgement
If your breasts feel hard, swollen, painful, and uncomfortably full, you’re likely suffering from engorgement, which can make it hard for your baby to nurse well. Engorgement is especially common in the early days of nursing, though it can happen any time. A little bit of engorgement isn’t a problem; your body will soon figure out that it’s producing more milk than your baby needs. But if you’re seriously engorged, you’ll want to take steps to relieve the pressure.
Pump or hand express just enough milk to make your breasts more comfortable. Nurse your baby frequently, and gently massage your breasts while breastfeeding. Use cold packs to relieve pain and swelling and heat (for just a few minutes before nursing) to help your milk flow.
Engorgement usually eases up in 24 to 48 hours. If yours doesn’t, or if you have signs of an infection (such as a fever), let your provider know.
Learn more about how to handle breast engorgement.
Clogged milk duct
If you have a tender, hard lump on your breast, you may have a clogged milk duct. This means that the breast milk is backed up in the tubes that carry milk to your nipples. The area around the lump may be red and feel swollen or hot, and you may feel some pain during letdown.
Clogged ducts can happen if you’re having trouble nursing – because of sore nipples or a poor latch, for example. Engorgement can also lead to clogged ducts, as your breasts become overfilled with milk.
To remedy the clog, keep nursing and/or pumping. Gently massage the area while nursing, and vary your nursing position. Eat well, drink plenty of water, and get rest.
Most clogged milk ducts will go away in a day or two. If yours doesn’t, it can cause other problems, such as mastitis. Talk with your provider or lactation consultant if your clogged duct doesn’t go away or if you have signs of an infection, such as fever, flu-like symptoms, or a larger area that’s tender and painful.
Read more about coping with a clogged milk duct.
Milk bleb or milk blister
If you have clogged ducts, you may also develop a milk bleb or milk blister. A milk bleb is a whitish or yellow-tinged spot or blister on your areola or at the tip of your nipple. You may have some redness or inflammation around the blister, and it may hurt when you breastfeed.
Milk blebs sometimes go away on their own, but if yours lingers, try warm or cold compresses, massage, and a little olive oil to soften the skin. Experiment with feeding positions, make sure your baby’s latch is good, and keep breastfeeding so it won’t cause breastfeeding problems. Don’t pierce the blister or you may cause an infection.
Call your provider if you develop any symptoms of mastitis, such as swelling, fever, or chills.
Learn more about how to treat a milk bleb and how to prevent them.
Mastitis
Mastitis is a painful inflammation of breast tissue which can be caused by an infection. Your breast may be red, swollen, warm, painful, and/or hard to the touch. If you have an infection, you’ll also probably have flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, and muscle aches.
Talk with your healthcare provider right away if you have symptoms of mastitis. You’ll need antibiotics if you have an infection. Though nursing can be painful with mastitis, try to continue to breastfeed. This will keep up your milk supply and help treat the condition.
Read our article on mastitis to learn how to nurse with mastitis, how to treat your symptoms, and how to avoid getting it.
Dysphoric milk ejection reflex
Some women experience something called dysphoric milk ejection reflex (D-MER) while breastfeeding. It’s caused by a drop in dopamine (the “feel-good hormone”) that occurs at the start of letdown. D-MER causes a range of feelings – such as sadness, anxiety, panic, and anger. (The feelings go away once the milk is flowing.)
For some women the response is mild, but for others it’s severe. For some, it goes away in a few weeks, and for others it lasts for the entire breastfeeding period.
If this happens to you, know that you’re not alone. One researcher estimates that as many as 9 percent of breastfeeding women experience D-MER. Talk with your healthcare provider or a lactation consultant about your symptoms.
Leaking breasts
Many nursing moms spray or leak milk when their breasts become overly full or when their letdown reflex responds unexpectedly. Sometimes just hearing your baby cry or thinking about them can cause leaking. (It’s because the hormone oxytocin kicks in.)
Leaking often happens when milk supply is at its peak (in the mornings, usually) and during feedings (you’ll leak from one breast while your baby nurses on the other). Tucking nursing pads in your bra will keep you dry, or you can collect your precious breast milk with a silicone breast pump.
If your milk squirts out when your baby starts to nurse, or if they fuss during feedings, you may have an overabundance of milk (hyperlactation), which causes milk to come out too fast. You may feel engorged, or have pain during letdown. You’ll probably also leak milk between feedings and abundantly from one breast while nursing from the other.
Read our article on what to do if your breasts leak milk for more information. You may also want to work with a lactation consultant until you and your baby are in synch.
Low milk supply
Low milk supply is a common worry while breastfeeding a newborn – and it’s important to make sure your baby is getting enough breast milk. If your baby stops gaining or begins to lose weight, or if they show any signs of dehydration (wetting fewer diapers, having dark urine and a dry mouth and skin), talk with their doctor right away.
If you’re having trouble with milk supply, the main thing to do is nurse and/or pump more to tell your body to produce more milk. Take good care of yourself, and get support – for your mental health and physical needs. A lactation consultant can help you identify any underlying problems that may contribute to your low milk supply.
Thrush
White spots or patches in your baby’s mouth that can’t be wiped off are a sign of thrush, a type of yeast infection that your baby can pass to you. Your baby may also cry when nursing, if the patches are painful, and they may have a yeast diaper rash.
If your nipples are pink, red, shiny, flaky, and/or cracked, or if you have itching, burning, or deep, shooting breast pain during or after feedings, you may also have a yeast infection
Some women and babies are more susceptible to yeast infections than others. Because you can pass the infection to each other, it’s important that both you and your baby are treated. You’ll both need an antifungal cream (prescription or over-the-counter) for the infection. If that doesn’t do the trick, you may need a stronger oral antifungal medication.
Read more about how to recognize and treat thrush when you’re breastfeeding, and learn about thrush in babies.
Difficulty taking a bottle after nursing and vice versa
Some babies switch back and forth between bottle and breast with no problem, but others have trouble. Your baby may be used to breastfeeding and want nothing to do with a bottle, despite the fact that you need them to take one.
Using paced bottle feeding (to mimic the flow of milk from the breast) and experimenting with bottle nipples, feeding positions, and milk temperatures may coax them along.
Learn how to get your baby to take a bottle.
Or, your baby may be less interested in nursing from the breast if they’ve been bottle feeding. That may be because they have to work a little harder at the breast than they do with a bottle. The problem may be exacerbated if your milk supply drops when your baby stops nursing as enthusiastically.
If your baby is reluctant to breastfeed after bottle feeding, try switching to a bottle nipple that has a slower flow and is shaped more like a breast nipple – and continue to breastfeed, too. You might also try nursing when your breasts are full, so that your baby will get the milk more quickly when they start nursing.
Preferring to nurse on one breast
It’s not uncommon for babies to develop a breast preference. Your baby may prefer one breast if it’s easier to latch on to or has a greater milk supply, for example. Or they may simply be more comfortable being held on one side than the other.
To coax your baby onto the less-popular breast, offer it when they’re just waking up and still sleepy. Also offer that breast first when they’re hungry. If the breast is engorged, making it hard for your baby to latch on, try hand expressing or pumping just a little bit of milk to soften it and make it easier for your baby.
If your baby insists on nursing from one side, be sure to pump the other side to prevent engorgement.
Read more about what to do if your baby only nurses on one side.
Refusing to nurse
Your baby may go on a nursing strike for many reasons, such as teething pain, a stuffy nose, an ear infection, or even a disrupted routine. These strikes usually last between two and five days, though they can continue longer.
Keep encouraging your baby to nurse, and also pump your milk about as often as your baby would normally nurse, in order to keep your milk supply up and prevent plugged ducts and engorgement. You might try offering your baby the expressed milk in a bottle, a sippy cup, a spoon, or a feeding syringe.
Keep track of your baby’s wet diapers (they should have at least six wet diapers daily). Check in with their doctor if you’re at all concerned that your baby isn’t getting enough nourishment.
Tongue-tie
A tongue-tie means that the soft tissue under your baby’s tongue (called frenulum) is short, keeping the tongue closely attached to the bottom of the mouth. In some babies, a tongue-tie can cause problems with feeding, because it’s hard for them to latch. A tongue-tie can also make it hard for a baby to move their tongue in the wavelike motions needed for effective breastfeeding.
If your baby has trouble latching on, makes clicking noises while feeding, or keeps breaking suction while feeding, they may have a tongue-tie. Another sign is nipple soreness due to the improper latch.
Ask your baby’s doctor or a lactation consultant to take a look. The condition is easy to correct with a quick, simple surgical procedure.
Gassy baby
Some moms are sure that when they eat certain foods – such as dairy products, cabbage, garlic, or spicy food – their baby experiences gas and fussiness. There’s not much scientific proof that there’s a direct correlation, and there are other reasons for a baby to have gas. Babies’ digestive systems are still developing, and they often swallow air when they nurse.
A small percentage of babies have a true allergic reaction to something in their mom’s breast milk (most often cow’s milk).
If you notice that your baby seems gassy and fussy when you eat a particular food, there’s no harm in avoiding it for a while.
How to find breastfeeding support
The good news is that most of the breastfeeding problems you encounter are issues you can solve. Reach out to your healthcare provider, your baby’s doctor, or a lactation consultant for help.
Read more about
Add a Comment