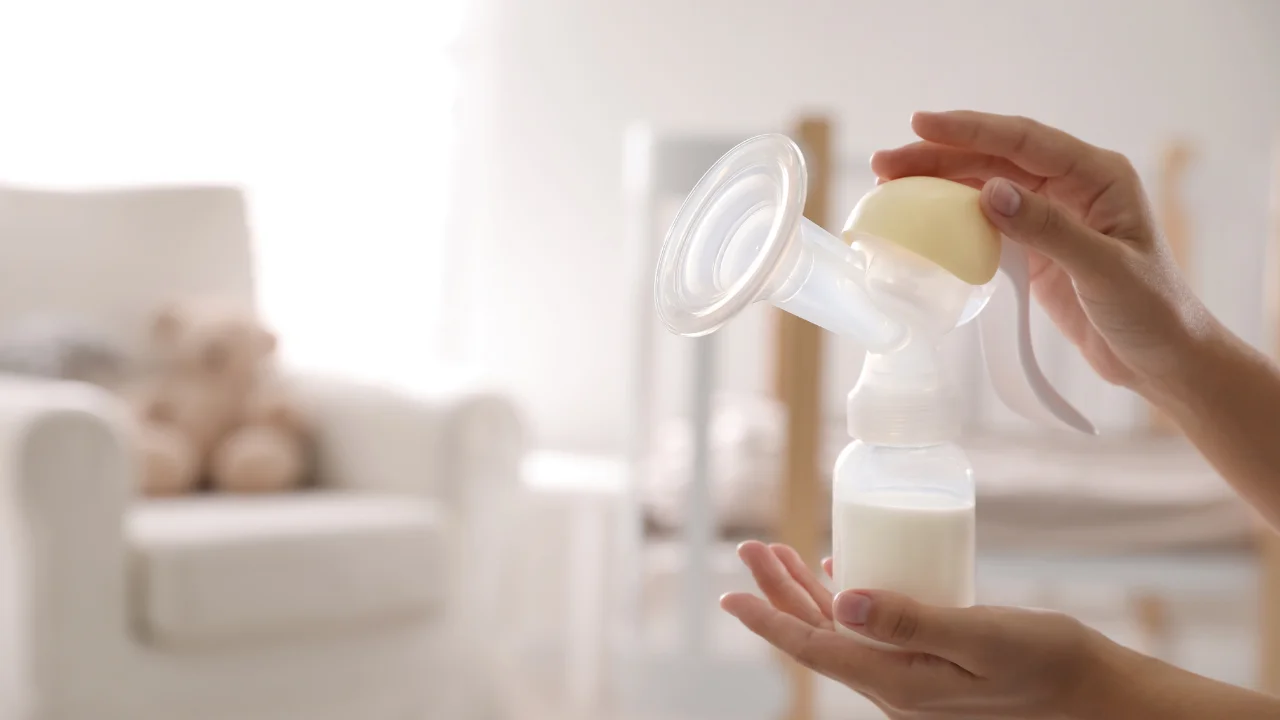

Exclusively pumping means only feeding your baby breast milk that you’ve pumped. You might opt for exclusively pumping if your baby can’t or won’t breastfeed, you want to share feedings with someone else, you need to be away from your baby, or you’re uncomfortable with breastfeeding. It’s a big commitment – an exclusively pumping schedule involves pumping around the clock – but by exclusively pumping you can give your baby the benefits of breast milk without nursing.
IN THIS ARTICLE
- What is exclusively pumping?
- How to exclusively pump
- Exclusively pumping pros and cons
- Exclusively pumping schedule
- Exclusively pumping tips
- How to increase milk supply when pumping exclusively
- Does exclusive pumping give babies the same benefits as breastfeeding?
What is exclusively pumping?
Exclusively pumping – sometimes called EPing – means that your baby drinks only your breast milk but doesn’t nurse. Instead, you pump or express your breast milk and then feed it to your baby in a bottle. Experts estimate that between five and six percent of moms feed their babies by exclusively pumping.
Here are some of the reasons you might choose exclusively pumping:
- Your baby can’t breastfeed (because of prematurity, hospitalization, physical issues such as cleft lip and palate or tongue tie, other difficulties latching)
- You’re returning to work or school or need to travel
- You’re having difficulty breastfeeding but not pumping (you find breastfeeding very painful, for example)
- You want to see how much milk your baby is drinking – because you’re worried about failure to gain weight or milk supply, for example. Or maybe you’re just more comfortable monitoring and scheduling your baby’s feeding amounts.
- You have multiples and want help with feedings
- You have a history of sexual abuse or other reason for discomfort with breastfeeding
- You want to share the feeding experience with others (a partner or spouse, for example)
- Your older baby is biting
- Your baby refuses to nurse
How to exclusively pumping
If you’re planning to exclusively pump, you’ll be expressing or pumping milk throughout the day. You can feed it to your baby right away, or you can store it in the refrigerator or freezer for later. Set up a comfortable place to pump and a clean area to store and sanitize your supplies. Consider buying extra parts for your pump so you always have a clean set ready to go.
You’ll need:
A good breast pump
A hospital-grade pump – which you can get at the hospital when your baby is born – will help get your milk supply established. A hospital-grade pump has a larger motor than other pumps, and it usually produces better, faster results. You can rent one from the hospital or from community breastfeeding centers. (Renting from the hospital is usually covered by insurance. This may not be true at centers, so you’ll want to check.)
Once your supply is well established, you can transition to a retail electric pump – available online or in stores. If you start to experience decreased production at any time, you may want to go back to a hospital-grade pump. (Some women with chronic milk supply issues continue to use the hospital-grade pump rather than transitioning to a retail pump.)
Look for a high-efficiency, electric pump that collects milk from both breasts at the same time. This will save you time and energy. Double pumping has been shown to raise the level of prolactin (the milk-producing hormone) in your body. Pumping from both breasts at once results in additional let down during a pumping session, more milk, and milk with a higher fat content.
Breast milk storage bags or bottles
Store your milk in the amounts your baby usually drinks in one feeding – say 2 to 4 ounces. Use bottles made of glass or hard plastic with tight fitting lids, or plastic bags made for storing breast milk. If you’re freezing the milk, leave room at the top for expansion.
Because exposure to light can decrease riboflavin (vitamin B2) and vitamin C levels, some experts recommend amber-colored storage containers for breast milk.
Breast milk can be stored at room temperature for four hours, in the refrigerator for four days, or in the freezer for six months. If you have a deep freezer, you can store your milk for 12 months. Date the milk you store, and use the oldest milk first.
Breast shields (flanges)
If the flanges that come with your pump aren’t comfortable, order a different size. A too-tight fit will compress milk ducts. Your nipples shouldn’t rub against the sides of the flanges during pumping. When trying the flange for size, keep in mind that your nipples will swell during pumping.
Some breast shields are made with a more comfortable design and material (silicone rather than hard plastic flanges that usually come with the breast pump) in a wide range of sizes, so experiment until you find flanges that are perfect for you.
Milk collection cups
These silicone cups tuck inside your bra to catch every drop of milk. They’re especially helpful if you’re pumping one breast at a time (the cup will catch any leaking milk from the breast you’re not pumping from). Or, some moms love manual silicone breast pumps for this purpose: These collect milk using suction with no effort from you.
Hands-free pumping bra
A trusty hands-free pumping bra will allow you to multitask while you’re pumping, so you can work, use your phone, or care for your baby. Note: Sometimes you can use the flaps of a regular nursing bra to hold breast pump flanges in place, too.
Hot/cold gel packs
Some moms find it useful to place a hot pack on their breast shield to encourage let down. Warm compresses also work.
Lactation massager
This vibrating massager can treat plugged ducts, reduce engorgement, and improve milk flow by improving milk letdown.
Pumping spray
Use this spray on the flanges of your pump to minimize friction and lubricate and moisturize nipples.
Nipple cream
Nipple cream can also be used to soothe and moisturize nipples and as a pump lubricant.
Feeding system
You may be feeding your baby breast milk from a bottle, or, in some cases, you may need another way to get the milk to their tummy. If your baby can’t feed enough by mouth (because they’re a tiny preemie, for example), they may need a nasogastric tube (NG tube) for feeding. The hospital staff will show you how to use this before you leave the hospital.
Exclusively pumping seems like a tall order, but it’s doable. One study of moms of preterm infants who were exclusively pumping showed that they could fully feed their babies by pumping six or more times a day.
Exclusively pumping pros and cons
Pros
- Your baby will enjoy the many benefits of breast milk.
- You have more control over your baby’s feeding schedule.
- Others can experience the bonding and closeness of feeding your baby.
- It provides flexibility to leave your baby as needed (for work, school, travel, etc.) and still provide breast milk for your baby.
- It’s less expensive than formula feeding, even accounting for necessary supplies.
- As long as you can successfully pump, there’s no worry about formula shortages.
Cons
- EPing is a big commitment. You need to pump regularly, around the clock (especially in the first few months), for it to work well. Cleaning pump parts and bottles and storing milk adds to the work.
- It can be difficult for some moms to produce enough milk. In one study, women who pumped but never fed at the breast were more likely to report difficulty producing enough milk than women who fed at the breast. They produced milk for a shorter time (an average of 56 days) than women who fed at the breast (who averaged 228 days).
- Exclusively pumping is more expensive than breastfeeding, because of the need for equipment and supplies.
- Breast milk that’s been pumped and stored isn’t identical to breast milk that a baby gets from nursing directly (see below).
Exclusively pumping schedule
Exclusively pumping requires diligence. It’s important to get off to a good start. And missing a pumping session can result in a decrease in milk supply.
When your baby is born, hand express your colostrum as soon as you can. (Colostrum is the first liquid your body produces for your new baby. It’s high in protein and antibodies and is your baby’s perfect first food.)
Hand expressing at this point has been shown to produce more colostrum than pumping. It may also be more comfortable and feel less intrusive right after childbirth.
Start using a breast pump, too, as soon as you’re feeling up for it – ideally in the first hour after birth, when a healthy newborn would normally nurse.
You may also want to try hands-on pumping, which means massaging your breasts and hand expressing while pumping. This will help maximize your milk supply while obtaining the most breast milk.
In 24 hours, pump at least 8 to 10 times, including overnight. Don’t worry about the small amount you’ll produce. Your baby needs less than an ounce per feeding for the first couple of days and then only an ounce or two per feeding for the first couple of weeks. Pump both sides for about 10 to 15 minutes.
Continue to pump for a minute or two after your breasts are emptied. (Or try to hand express after pumping.) This will help stimulate your milk production. Don’t pump longer than a total of 20 to 30 minutes, though, or your nipples may become sore
Going forward, continue to pump as often as you need to in order to reach a full milk supply for your baby. For most babies (depending on size and age) this is about 24 to 30 ounces a day.
You may eventually be able to drop a pumping session (say, one overnight session) without reducing your supply. You can try it and if your milk production drops, go back to more sessions.
Moms produce different amounts of milk, and babies’ needs are different. Some moms might eventually pump a handful of times each day and have plenty of milk for their babies, while others need to continue to pump 8 times or more daily.
There are apps to help you keep track of your pumping schedule.
Exclusively pumping tips
Some things to keep in mind:
- Stay hydrated and eat well. You need nutritious meals and snacks and plenty of water throughout the day. Read our tips for a healthy breastfeeding diet.
- Having skin-to-skin contact with your baby before or during pumping, when possible, can help your body release oxytocin and enable you to express more milk.
- When you can, make pumping a pleasant time by doing something you enjoy while pumping. Listen to music, meditate, look at pictures of your baby, watch funny videos, shop online, or sip warm nursing tea.
- Set the pump suction to a comfortable setting. Painful pumping inhibits the flow of milk.
- You’re likely to produce more milk if your pump simulates the sucking pattern of babies – starting at a rapid speed and transitioning to a slower speed. Some pumps do this automatically, but if yours doesn’t you can manually adjust to a slower speed once you feel your milk letting down.
- If you’re having trouble getting your milk to flow, try taking a warm shower or applying warm compresses on your breasts before pumping. Warming your pump flanges may also help.
- To keep from overfeeding your baby (and to give them more control), pace feed them. Paced feeding means you feed your baby in a way that mimics the flow of breastfeeding. Keep the bottle horizontal, for example, so the milk flows as your baby sucks, and pause frequently during feeding. Stop feeding when your baby shows signs of being full.
- If you need to increase your milk supply in a hurry, simulate cluster feeding (something babies do occasionally, sometimes when they’re having a growth spurt) by pumping for an hour with a few short breaks. For example, you might: pump for 20 minutes, wait 10 minutes, pump for 10 minutes, wait 10 minutes, pump for 10 minutes. This is also called power pumping. Power pumping for a few days will probably do the trick.
- Don’t rely on exclusively pumping as a LAM (lactational amenorrhea method) of birth control. LAM only works for the first six months of exclusive breastfeeding, not pumping.
- When considering birth control, tell your healthcare provider that you’re exclusively pumping. Some birth control methods contain estrogen, which can affect your milk supply.
How to increase milk supply when exclusively pumping
If your milk supply seems to be decreasing:
- Pump more often. The more you pump – which simulates your baby nursing – the more milk your body produces in response. If you’ve been pumping a little less, go back up to 8 to 12 sessions every 24 hours. If you’re pumping as usual and your production has slowed, add a session or two. Pump more frequently rather than longer at each session.
- Try pumping extra milk in the morning. Most women are able to pump more milk in the morning than later in the day.
- Feeling upset, angry, or stressed can inhibit your milk flow. Take a break and pump later, when you’re feeling calmer and more relaxed.
- Pump for another two or three minutes after you see the last drops of milk.
- Try a galactagogue (food or drink to increase milk supply). There’s no scientific evidence that these work, but there’s no harm in trying. Galactagogues include foods (like oats, barley, garlic, seaweed, and millet) and herbs (like basil, blessed thistle, and fennel). Read more about galactagogues and other ways to increase your milk supply.
- Talk with a lactation consultant. They can give you personalized tips for increasing your milk supply and help with any problems you’re having with your pump.
If you still don’t produce enough milk, consider supplementing with formula. Don’t combine the two in a bottle, though. Give your baby your breast milk first, then follow up with the formula. (There’s no health danger in combining breast milk and formula, but you don’t want to waste any breast milk if your baby doesn’t polish off the combination bottle.)
Does exclusively pumping give babies the same benefits as breastfeeding?
Breast milk – from breastfeeding or from a bottle – is the ideal first food for your baby. It provides your baby with optimal nutrition, immunity, digestive benefits, and more.
Researchers are studying potential differences between breast milk that a baby drinks from a bottle and breast milk that a baby drinks from the breast. While breast milk is still best for your baby, they’re not identical. For example:
- Pumped breast milk has a higher risk of bacterial contamination than direct breastfeeding or hand expressing. This may affect an infant’s gut microbiome, crucial to the development of their immune system. You can minimize this risk – which exists with formula feeding, too – by washing your hands and pump parts with soap and warm water.
- Some small studies suggest that using pumped breast milk may increase the risk of ear infections, diarrhea, respiratory infection and asthma, coughing and wheezing – when compared to nursing directly at the breast. These risks are also greater with formula feeding, however, so breast milk from a bottle is still better for your baby.
- Because bottle-fed babies tend to drink more, some researchers suggest that EPing may increase an infant’s risk of becoming overweight or obese in childhood. (This is true for both babies who drink formula and those who drink breast milk from a bottle, but it’s more evident in formula-fed babies.) You can address this by following your baby’s feeding cues and using paced feeding.
- Fresh milk contains more antibodies, antioxidants, vitamins, protein, fat, and probiotic bacteria compared to refrigerated or frozen breast milk. When you can, give your baby the freshest milk, which will have the least deterioration.
In addition, breast milk corresponds to a mom’s (and a baby’s) circadian rhythms. These rhythms can affect sleeping, growth, and development. For example, day milk has more cortisol and amino acids that promote alertness, while night milk has more melatonin and tryptophan to help foster sleep. You may want to label your breast milk storage containers with the time of day when the milk was pumped and feed it to your baby at the corresponding time.
Read more about
Add a Comment