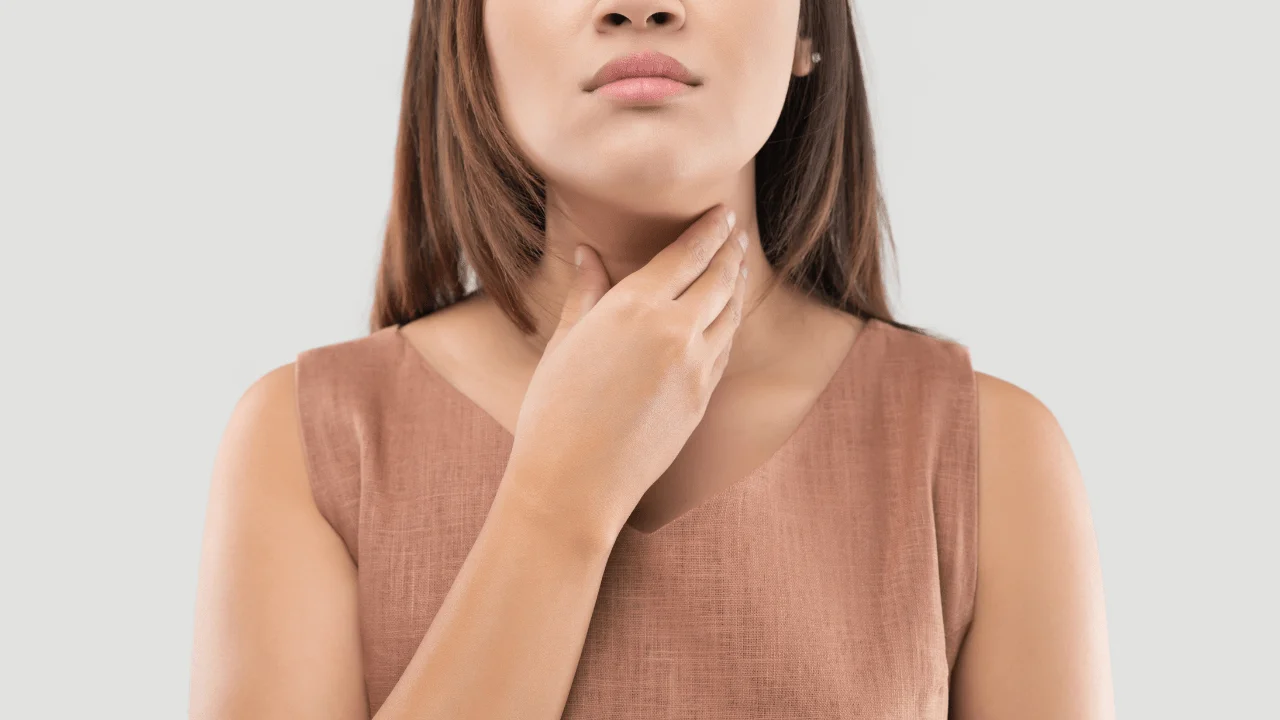

Postpartum thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland that happens in the months following childbirth. Some women will experience a few months of hyperthyroidism followed by several months of hypothyroidism, while many others will go through either one or the other. Symptoms are usually mild, though more severe hypothyroid issues can often be treated with medication to replace the missing thyroid hormone. Most of the time, postpartum thyroiditis is temporary, mild, and gets better all by itself.
IN THIS ARTICLE
- What is postpartum thyroiditis?
- What causes postpartum thyroiditis?
- What are the symptoms of postpartum thyroiditis?
- What are the risk factors for postpartum thyroiditis?
- When will I experience postpartum thyroiditis?
- Postpartum thyroiditis treatment options
What is postpartum thyroiditis?
Postpartum thyroiditis occurs when your thyroid gland becomes inflamed in the months following childbirth. It happens in women without previous thyroid disease.
Your thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped organ located in the lower front of your neck, slightly above the collarbone. Its job is to produce triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), hormones that control how your body uses energy. Among their many functions, these chemicals help regulate your heart rate, body temperature, weight, and menstrual cycles.
When you have postpartum thyroiditis (“itis” means “inflamed”) your thyroid produces either too many hormones (hyperthyroidism) or too few hormones (hypothyroidism). Or, you go through two distinct phases – first hyperthyroidism, and then hypothyroidism.
The condition affects about 5 percent of pregnant women and often gets better within 12 to 18 months, many times without treatment. While some people experience severe symptoms, most people have only mild symptoms – or none at all. Postpartum thyroiditis is usually a temporary problem, but it leads to lifelong thyroid issues in about 20 percent of women affected.
What causes postpartum thyroiditis?
Many experts believe postpartum thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease similar to another illness called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. They’re almost impossible to tell apart, and antithyroid antibodies are present in both conditions.
What are antithyroid antibodies, exactly? Well, antibodies are proteins your immune system creates to fight bacteria, viruses, and other invaders. Occasionally, they target things they’re not supposed to – like your body’s cells and organs. In the case of antithyroid antibodies, they specifically attack thyroid tissue, resulting in inflammation and dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
What are the symptoms of postpartum thyroiditis?
There are two phases of postpartum thyroiditis. The first phase is hyperthyroidism, while the second is hypothyroidism. About one-quarter to one-third of women will experience both phases (the classical presentation), while the remainder will go through one or the other.
The first phase (hyperthyroidism) starts two to six months after childbirth and lasts for up to three months. During this period, the majority of women don’t experience symptoms. From time to time, some may have mild, temporary issues like muscle weakness, insomnia, heart palpitations, poor focus, or intolerance to heat. They may feel irritable or anxious. Occasionally, hair loss and/or weight loss can occur that are different and more pronounced that the normal postpartum hair thinning (telogen effluvium) and natural weight loss postpartum.
Postpartum thyroiditis is commonly missed during this first phase (hyperthyroid phase), often because there are no symptoms. But sometimes it’s because many women have these issues after becoming a mom, anyway – they’re frequently part of the postpartum period, so a health condition is never suspected.
During the second phase of postpartum thyroiditis (hypothyroid phase), most women experience symptoms. They typically begin 3 to 8 months after childbirth and can include:
- Fatigue
- Loss of memory or focus
- Dry skin
- Muscle weakness
- Aches, pains, and cramps
- Tingling or prickling sensations (pins and needles)
- Constipation
- Depression
- Problems with exercising
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Weight gain
In about 80 percent of women these symptoms go away on their own after about 9 to 12 months. In the remaining 20 percent, the hypothyroidism never resolves, and they need a more long-term thyroid hormone replacement medication on a daily basis.
If you’re high-risk for postpartum thyroiditis (see below) and you develop symptoms, it’s essential to speak with your healthcare provider. To reach a diagnosis, they’ll consider your symptoms and test the thyroid hormone levels in your blood. They’ll also need to rule out other illnesses. For example, postpartum thyroiditis can look a lot like Graves’ disease. But it’s a separate autoimmune condition that follows a different course and doesn’t have the same treatments.
Since postpartum thyroiditis occurs after delivery, it will not affect your baby.
What are the risk factors for postpartum thyroiditis?
The biggest risk factor for postpartum thyroiditis is a high level of antithyroid antibodies. Women who have them before becoming pregnant have an increased risk of the condition. The greater the number of antibodies, the greater the chances of eventually developing thyroid dysfunction.
Other risk factors include:
- Autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes, lupus, multiple sclerosis, Graves’ disease, and chronic viral hepatitis
- A personal or family history of thyroid dysfunction
- Having postpartum thyroiditis previously
Screening for postpartum thyroiditis is recommended by the Endocrine Society if you are high-risk. It’s not recommended for every pregnant woman.
Postpartum thyroiditis cannot be prevented, nor can you lower your risk of developing the condition.
When will I experience postpartum thyroiditis?
Postpartum thyroiditis can begin up to six months after you’ve given birth. The first phase lasts for up to three months, while the second phase often goes from 9 to 12 months. Normal thyroid function resumes between 12 and 18 months for about 80 percent of women. The other 20 percent will develop long-term hypothyroidism, easily treatable with daily thyroid hormone supplementation.
Postpartum thyroiditis treatment options
Typically, there is no treatment for the first phase of postpartum thyroiditis. It usually resolves on its own. If you have severe symptoms, you may be prescribed beta blockers.
Treatment for the second phase will hinge on your age and overall health, as well as your symptoms and the severity of your hypothyroidism. In general, people with mild symptoms will be monitored, but not treated. Women who are nursing or attempting to conceive are the exception, and may receive thyroid hormone replacement medication. Women with more serious symptoms will also be started on thyroid hormone replacement and monitored.
Since postpartum thyroiditis is temporary and usually mild, most women won’t need treatment for either phase. Your provider will continue to regularly test your thyroid levels, however, since some people do develop permanent thyroid dysfunction. If your hypothyroidism persists, your physicians will start you on daily thyroid hormone replacement.
Read more about
Add a Comment