3-Weeks-Old Baby
3-Week-Old Baby
Your baby's not trying to torture you with all that crying —
she's just trying to tell you something.
Highlights
Your baby is starting to transform from a precious-but-super-sleepy newborn to an almost full-fledged infant. And with all that growth and development happening, there are some big changes and milestones coming down the pike.
So get excited! Payback for the sleep deprivation you’re probably dealing with is on its way. Here’s what you can look forward to this week.
Your 3-week-old baby's development
Week 3
Baby’s Development

Your little one is getting stronger every day — and you can encourage baby to flex those muscles by providing ample supervised tummy time during the day so she can practice lifting that cute head.
Some 3-weekers will be able to lift their heads 45 degrees when on their tummies, and the more practice baby gets, the better.
Tummy time will also help prevent head flattening, something more common in babies who spend all day and night lying on their backs or propped in bouncers and car seats.
In brain-related news, your baby is ready for more complex shapes (bye-bye circles, hello zigzags!) as vision, the ability to focus, and concentration improve rapidly. She may really love gazing at a mobile or a soft toy you hold up close enough so she can see it.
Of course, when she’s not in the mood to play, she might be in the mood to cry (and cry). All babies cry, but some babies wail more than others.
In fact, there are newborns who sob inconsolably for hours. Doctors will generally diagnose such crying as colic when it lasts for at least three hours at a time, at least three days a week, over the course of at least three weeks.
At a Glance

Sleeping basics
Newborns up to 3 or 4 months old need 14 to 17 hours of sleep in a 24-hour period, usually waking every two to four hours to eat.

Feeding basics
Breastfed babies should eat as much as they want at this age, but a general rule of thumb is roughly 16 to 24 ounces of breast milk or formula in 24 hours.

Did you know?
Your little one is gaining muscle control, so those movements and reflexes will become less jerky and more graceful this week.
Your 3-week-old baby's growth

Your cutie is surely packing on the pounds and ounces now that she’s 3 weeks old. But when taking note of your little one’s weight, stop yourself from comparing it to your BFF’s baby’s weight, or your sister’s, or … you get the idea.
That’s because the most important measure of your baby’s growth isn’t how she stacks up to other babies, but rather how she stacks up to her own weight and height curve.
The pediatrician will want to follow your baby’s growth trends over time. The doctor will look closely to make sure your little one is trending on relatively the same curve she’s been on (whether that’s the 15th percentile, the 50th percentile or the 90th percentile).
A big jump (say, from the 20th percentile to the 50th percentile) can mean that baby’s gaining too fast. A big dip can mean she isn’t getting enough to eat.
Your baby’s doctor will help you make sense of these percentiles and how your baby is growing.
Your 3-week-old baby's health
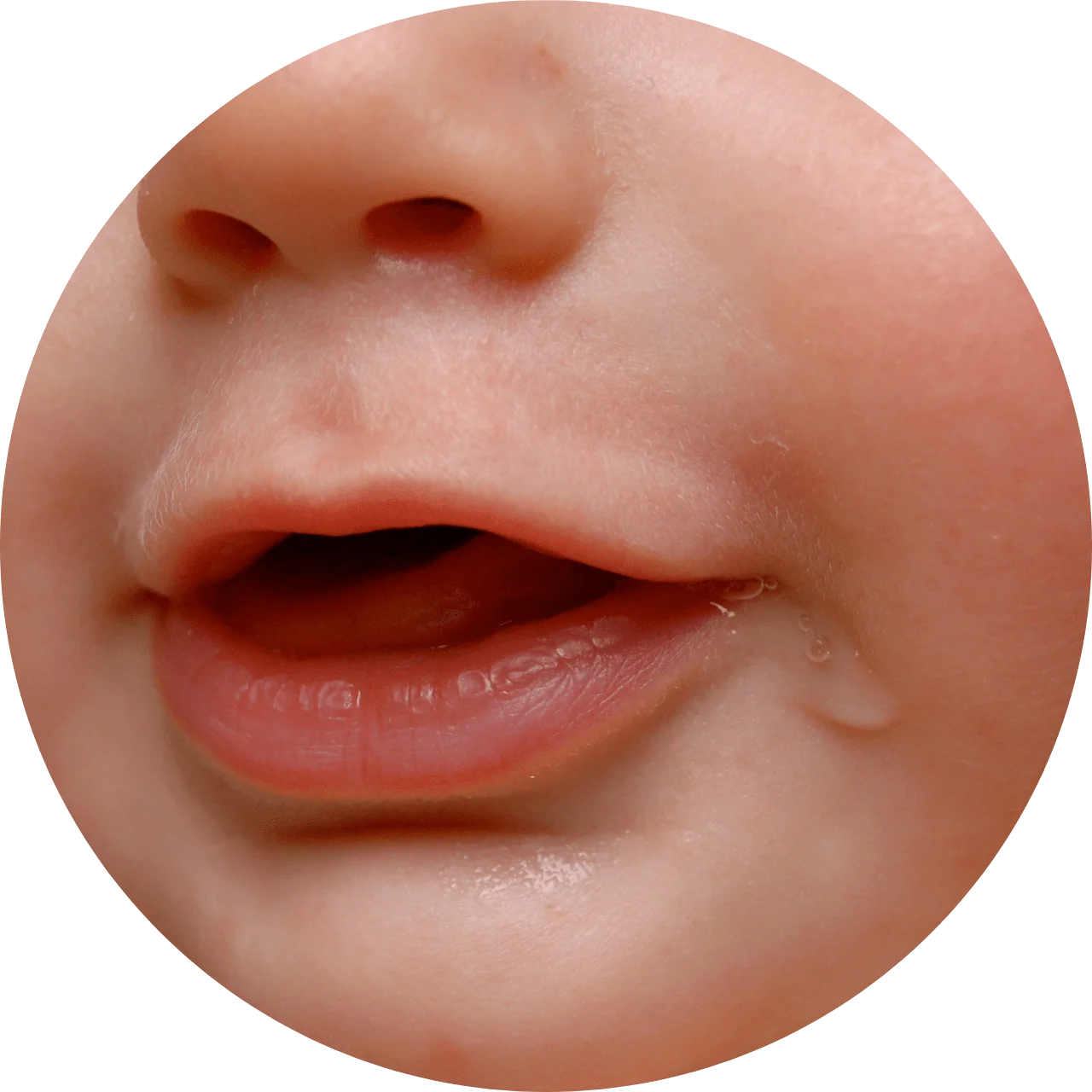
Spitting-up baby
Don’t be alarmed if baby is spitting up a lot. What looks like her entire lunch is probably no more than a tablespoon of milk. Things should calm down in a month or two.
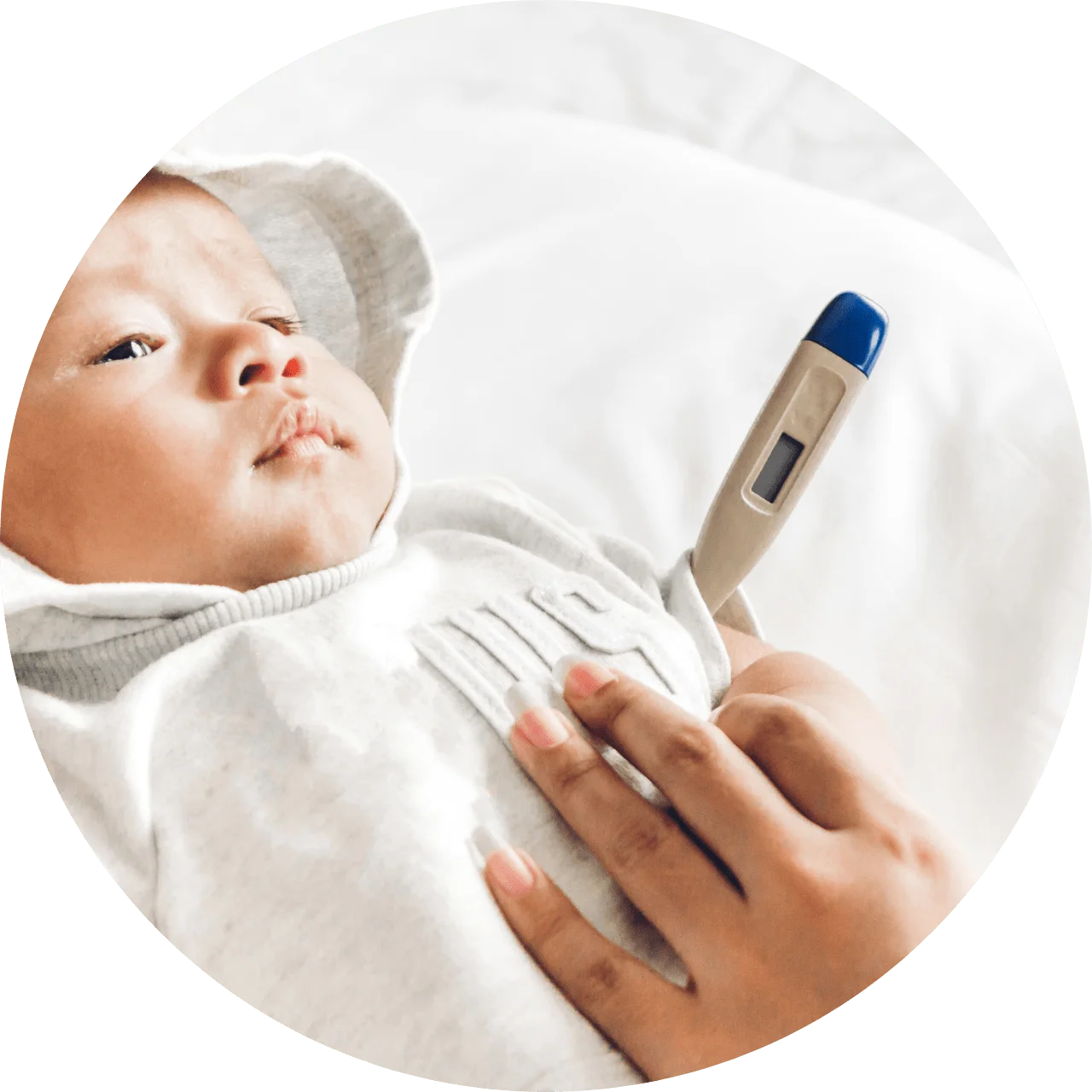
Baby fevers
A temperature under 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit in babies this age is not considered a fever and is nothing to worry about, but anything 100.4 degrees F or higher warrants a call to the doctor right away.
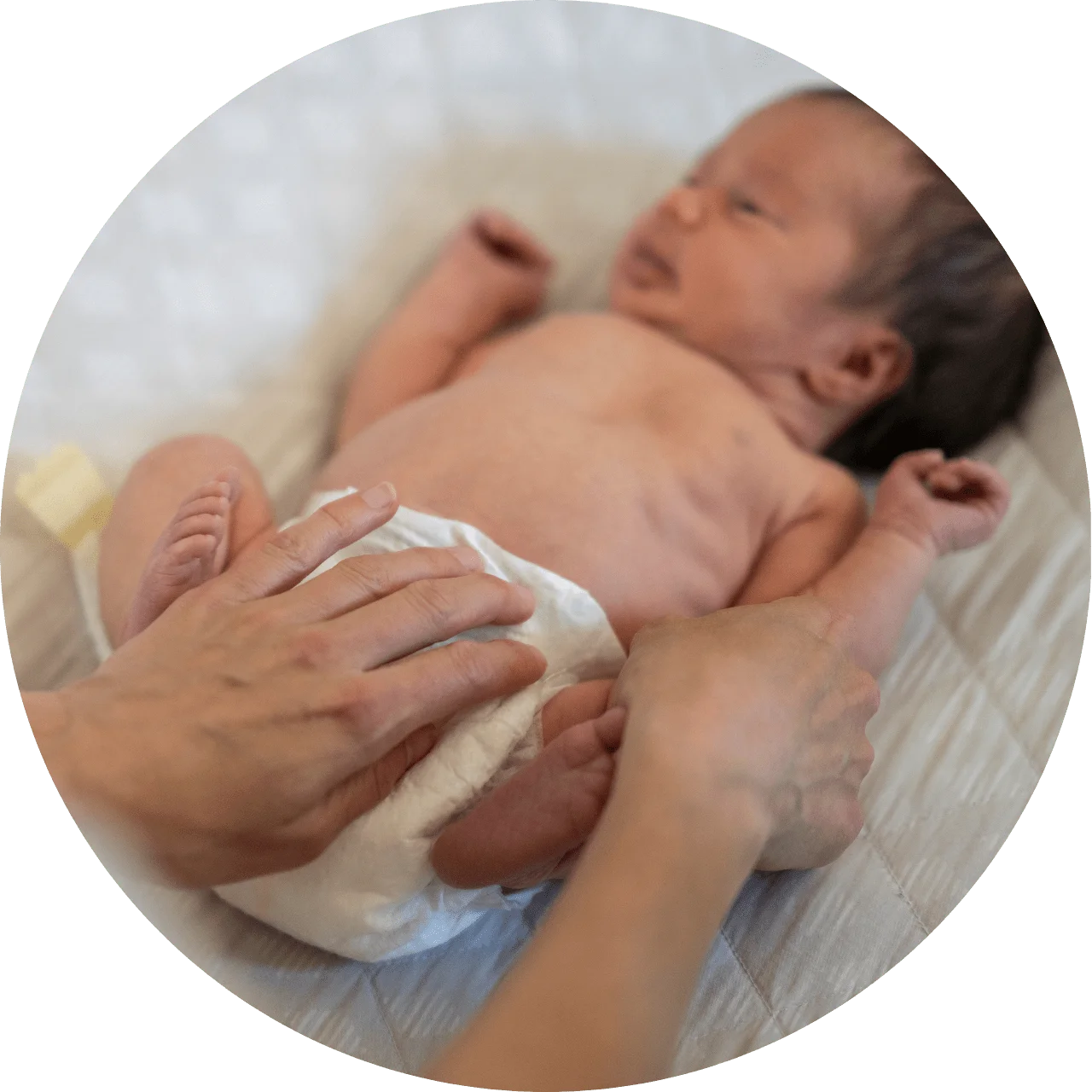

The scoop on poop
If your baby is breastfed, her bowel movements will probably be mustard-colored, loose and sometimes seedy. In formula-fed babies, the stool will be probably be soft, and can range anywhere from pale yellow to yellowish brown, light brown or brownish green.
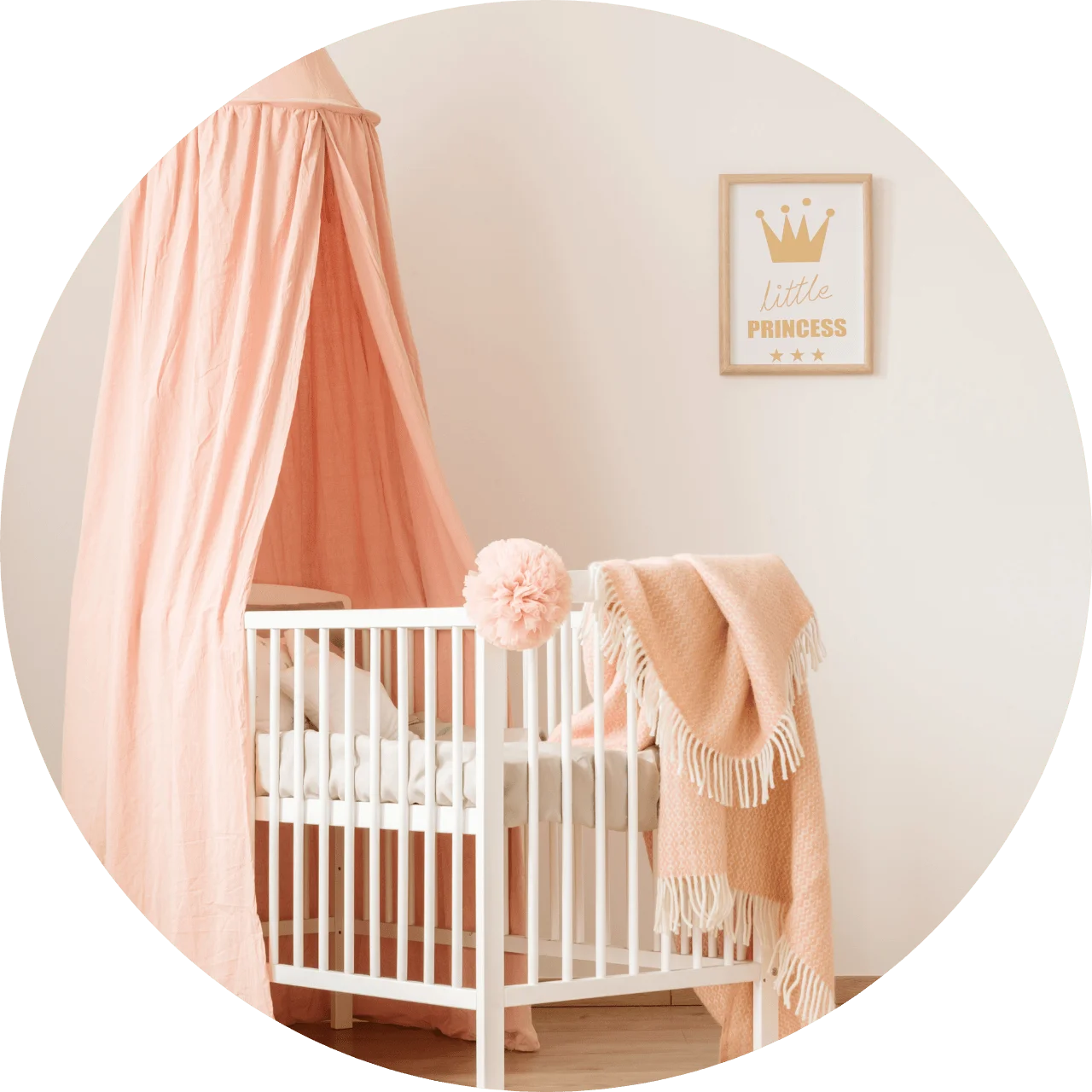

Crib safety
Your baby will be spending a lot of time in that crib, so you’ll want to make sure it’s safe. A crib should meet the latest standards set by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC).
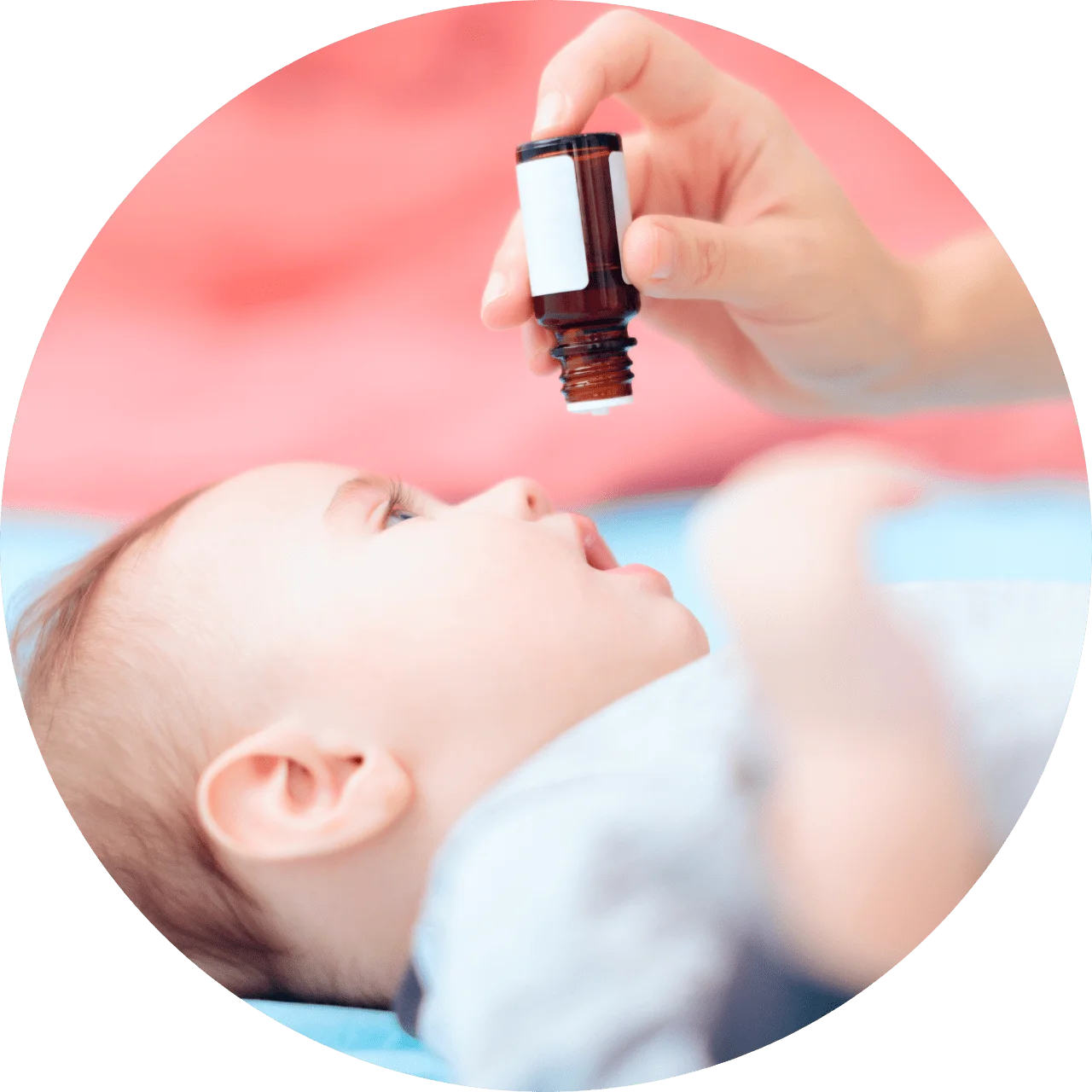
Vitamin D for baby
Newborns and older babies need 400 IUs of vitamin D each day. If your baby is breastfed, she’ll need to take vitamin D drops. While formula is already supplemented with vitamin D, ask your pediatrician if you should add vitamin D drops to your formula-fed baby’s bottle.
Postpartum & new baby tips
Milk bank FAQs
If you’re not able to breastfeed, and your baby has a medical condition that requires human milk (including prematurity, failure to thrive, an intolerance to formula or allergies), there are ways to get donated breast milk from other moms through a milk bank.
Here’s what you’ll want to keep in mind as you begin your search:
- As tempting as it may be, best friends (or even casual ones) shouldn’t become “breast friends.” The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), La Leche League and other experts frown on moms casually breastfeeding one another’s babies and for good reason: There’s always a risk that your pal could unwittingly pass on a virus or like hepatitis or HIV. There’s also the chance that the shared milk could contain medications if your friend is taking any.
- Do consider buying from a milk bank. Unlike an informal arrangement between moms, the milk banks in the U.S. have strict guidelines — guidelines that were set up by the Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA), an organization of pediatricians and other health care workers. The guidelines regulate donors as well as the way milk is collected and stored.
- Calculate the costs and get some financial help if you need it. Buying donated milk is expensive. Although nursing moms donate their milk for free, the milk, which the guidelines state can be obtained only with a prescription from your doctor, costs about $3 an ounce.
Soothing baby’s skin
While older babies are known for their smooth complexions, 3-week-olds definitely aren’t.
Among the conditions that may be keeping the skin your baby’s in colorful but less-than-flawless: red pimples and whiteheads (didn’t expect those until middle school at least?), pink diaper rashes, flaky cradle cap and purplish mottling (not to worry — it’s just a sign of your baby’s immature circulation).
Fortunately, all these baby skin imperfections are temporary. Some, like the pimples and mottling, will go away on their own; others, like diaper rash and cradle cap, will respond well to treatment. Clear baby skin is just around the corner.
Fecal incontinence
Labor and delivery, as you might have noticed, are really rough on your body — especially “down there.” Your perineum muscles and nerves may be stretched or damaged, making it difficult for you to control how and when digested food leaves your body.
Postpartum fecal incontinence usually takes care of itself as your body returns to normal. Until then, here are a few steps you can take to alleviate the problem:
- Eat a gas-conscious diet. Skip hard-to-digest foods for now (nothing fried, no beans, no cabbage), and avoid overeating or eating on the run.
- Do your Kegels. Then do them again…and again. Kegels are just the ticket for tightening up those muscles, as well as the ones that control urine, which may also be leaking these days.
- Don’t be shy. Talk to your practitioner if the problem persists. Your health care provider might suggest a mind-body technique called biofeedback or possibly surgery if the situation is particularly bad, which it rarely is.
Newborn care during outings
It pays to be extra careful for the two months until your baby has had her first set of vaccines and her immune system is more developed. The younger your baby, the less time that tiny immune system has had to strengthen. That goes double for infants born prematurely or with other health concerns.
So in those early weeks, avoid crowded areas. Inside or out, keep your baby in a stroller, sling or carrier. And after any outing, clean your baby’s hands with a wipe or wet, soapy cloth.
Baby mixing up day and night?
If your little one keeps mixing up day and night, try these tips:
- Limit daytime snoozes to three-hour stretches. That way she won’t get into the habit of bunching up sleep during the day. Even though your newborn doesn’t have a naptime routine yet, you probably will want to wake your baby up to eat every three to four hours or so anyway at this age. If you have trouble rousing your drowsy darling, try these tactics: Hold your baby upright, unswaddle your little one, strip off some clothes, tickle those little feet or hands, stroke that cute face, move baby’s arms and legs, or put a cool washcloth on the forehead. If all else fails, try changing baby’s diaper — that’s usually a surefire way to wake up a little sleepyhead. Once she’s awake, keep your little one alert by singing upbeat songs and dangling toys in front of baby’s face.
- Make your newborn’s naptime routine slightly different from the nighttime one to help your baby distinguish between the two. Though you’ll want to establish a wind-down routine for naps that’s similar to the one you use at bedtime, adjusting it a bit during the day can clue your baby in that it’s not time to turn in for the night. Keep a shade or curtain open a little, for instance, so the nursery’s not pitch-dark. And don’t go overboard in terms of tiptoeing around while she’s napping, either (though you should do the opposite at night). Hearing some ordinary sounds while she’s snoozing, within reason, can help reinforce the difference between day and night.
- Don’t ditch naps. While it is important to teach your sleeping angel that nighttime is the best time for snoozing in long stretches, she’ll still need to fit in some shut-eye during the day. The average baby sleeps at least 14 to 17 hours in a 24-hour period, so lots of that infant rest needs to happen during the day. And be grateful that your baby seems to know how to power-nap at all — it’s a good sign that she’ll learn how to sleep through the night in the not-too-distant future.
Hand washing for friends
Your friends and family are probably as excited to meet your newborn as you are to show your little bundle off.
But be sure to set and enforce this simple ground rule: All admirers who want to touch or hold your baby must wash their hands first — and anyone who is clearly sick or has a rash should stay home.
Blame your pediatrician or your own paranoia, but get your message across. Be especially careful with small children, who could be carrying all sorts of contagious stuff.
Teach them to gently pat your baby’s back or touch her tiny toes, but never the hands or face. And after any outing or social scene, clean your baby’s hands with a wipe or wet, soapy cloth.
Baby’s cries, explained
Most babies pick a fussy period during the afternoon or early evening as their “witching hour” to let it all out and cry for a while.
If the crying is colic (which it isn’t always), it may seem like those babies are in pain. One theory is that colicky babies are also gassy babies, though they might be gassy because they’re swallowing a lot of air from all that crying or because newborns often struggle with gas pain because of their immature digestive systems.
Colicky babies also often seem to want to eat all the time — but sometimes that’s because the sucking is soothing, not because they’re hungry. Using a pacifier can help.
Your baby’s tearful bouts could be a sign that she’s overstimulated. Babies this age often need to unwind with a good cry at the end of the day.
She could also be hungry more often because she’s going through a growth spurt or for some other reason. Try feeding her a bit more and see if that helps.
If your baby does seem to be in pain, check for fever and call the doctor. It’s possible that she’s coming down with something.
But if it’s colic that she’s coming down with, it’s probably here to stay, to some degree, for the next few weeks or months. And if it’s hunger, work with your pediatrician to figure out whether any adjustments in the feeding department are in order.
Items Recommendation
-

Onesies
Br50.00Add to Wishlistወደ ጋሪው አክል፡ "%s"Add to Wishlist -

Stroller
Br32.00Add to Wishlistወደ ጋሪው አክል፡ "%s"Add to Wishlist -
Sale!

Baby bottle
Br25.00 – Br30.00Add to WishlistSelect options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageAdd to Wishlist



















Add a Comment